
GREP WILDCARD OPERATOR PC
The dir command with a glob pattern in IBM PC DOS 1.0. Also supported by the JS libraries and Python's glob. globstar: allows ** on its own as a name component to recursively match any number of layers of non-hidden directories.
The GNU fnmatch and glob has an identical extension. It can be enabled by setting the extglob shell option.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/WildcardSearch-5b33c17d46e0fb0037dfd8b3.png)
It is only expanded on the command line before globbing.
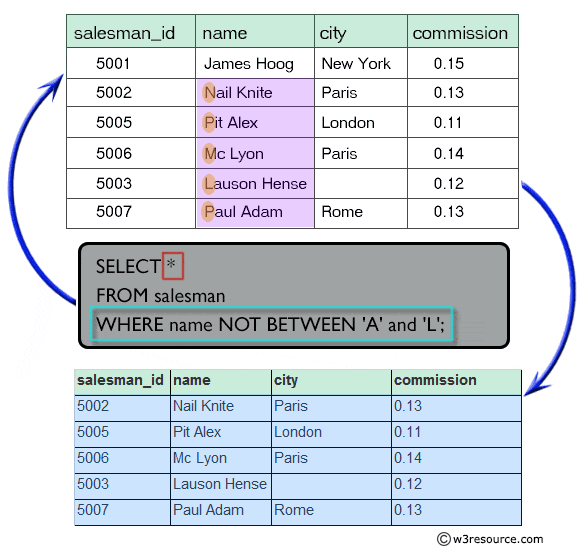
Because it is not part of the glob syntax, it is not provided in case. Some shells (such as the C shell and Bash) support additional syntax known as alternation or brace expansion. The POSIX-mandated case statement in shells provides pattern-matching using glob patterns. Globbing is provided on filenames at the command line and in shell scripts. Unix globbing is handled by the shell per POSIX tradition. They are defined to match up with the brackets in POSIX regular expressions. The ranges are also allowed to include pre-defined character classes, equivalence classes for accented characters, and collation symbols for hard-to-type characters. Letter1, Letter2, Letter6 up to Letter9 and Letterx etc. Matches one character that is not from the range given in the bracket Matches one character that is not given in the bracket On Unix-like systems *, ? is defined as above while has two additional meanings: Wildcard Some shells, such as Bash have functionality allowing users to circumvent this. Normally, the path separator character ( / on Linux/Unix, MacOS, etc. Matches one character from the (locale-dependent) range given in the bracket Matches one character given in the bracket Matches any number of any characters including none For example, * matches all visible files while. Traditionally, globs do not match hidden files in the form of Unix dotfiles to match them the pattern must explicitly start with. The idea of defining a separate match function started with wildmat (wildcard match), a simple library to match strings against Bourne Shell globs. Both functions are a part of POSIX: the functions defined in POSIX.1 since 2001, and the syntax defined in POSIX.2.
GREP WILDCARD OPERATOR SERIES
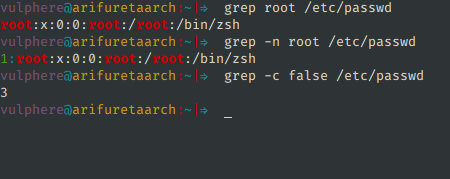
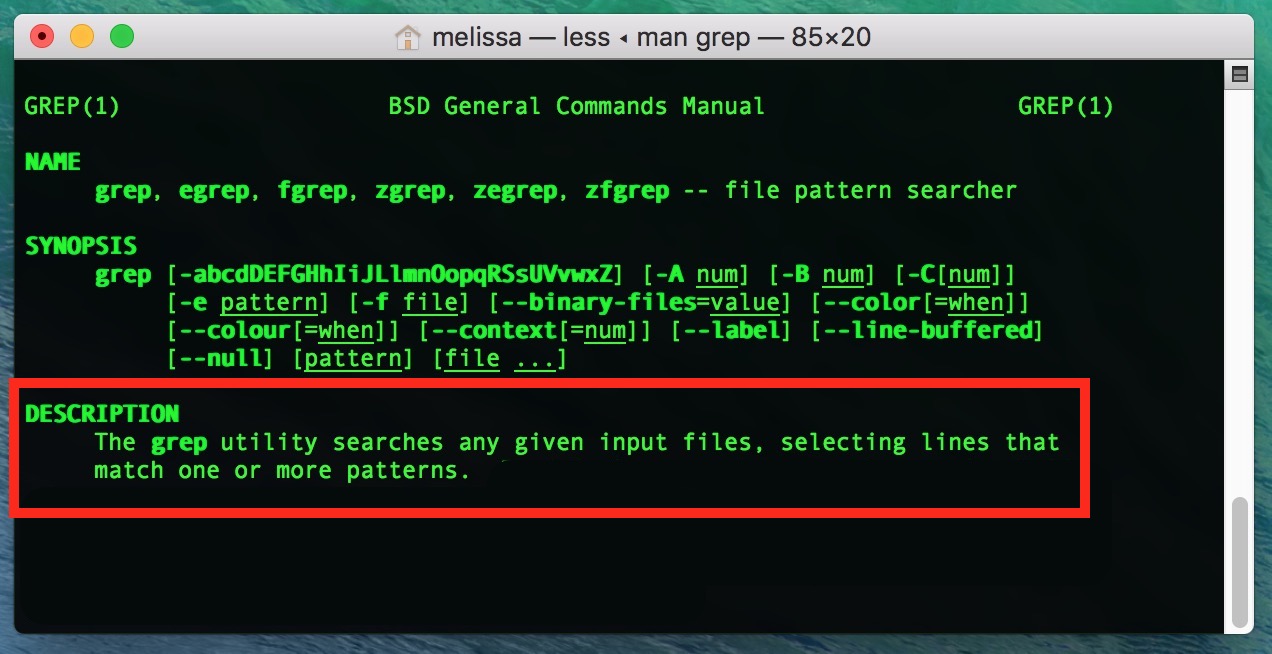
It is usually defined based on a function named fnmatch(), which tests for whether a string matches a given pattern - the program using this function can then iterate through a series of strings (usually filenames) to determine which ones match. Later, this functionality was provided as a C library function, glob(), used by programs such as the shell.
GREP WILDCARD OPERATOR SOFTWARE
It was the first piece of mainline Unix software to be developed in a high-level programming language. Glob was originally written in the B programming language. That program performed the expansion and supplied the expanded list of file paths to the command for execution. The command interpreters of the early versions of Unix (1st through 6th Editions, 1969–1975) relied on a separate program to expand wildcard characters in unquoted arguments to a command: /etc/glob. The glob command, short for global, originates in the earliest versions of Bell Labs' Unix. A screenshot of the original 1971 Unix reference page for glob – the owner is dmr, short for Dennis Ritchie.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
